
Learner-centricity is a hot topic right now. Although many organizations claim that their solutions keep the learner at the center of everything they do, reality is often a different matter. Consider the roles in the typical design flow: Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) focus on content (all the content!) that needs to be tied into a learning solution. Learning and Development (L&D) Managers focus their efforts on one delivery channel—mostly eLearning—and want to ensure learners pass the final quiz with 80%. Add to the mix Instructional Designers and Developers, who often work within a company-branded template that leaves little room to be creative and innovative. When you look at an organization from this angle, you might notice a missing factor: How can the design make a difference in a learner's life? How can organizations truly become more learner-centric? Enter human-centered design (HCD).
Human-centered design is intentional. It focuses on a user’s emotions and feelings as they interact with a product. For example, a human-centered design might begin by asking, “How do the learners feel when they take this training?” and “What do they think?”
HCD is designing with the end-user in mind, bringing empathy to the design process. When organizations embed human-centered design into their day-to-day design and development, they are prioritizing the experience of their diverse, empowered teams and of their customers.
According to IBM, if you bring your learners into the design process from the beginning, your focus shifts to drive better experiences for them. You build employee resilience and allow innovation to be less risky. It shows that you invest in your employees and the community around them.
There are several elements that differentiate traditional design approaches from HCD:
|
Target Audience |
Traditional design focuses on an abstract and fixed audience, whereas HCD is much more dynamic and includes users in its design. |
|
Measurement |
Traditionally, L&D looks at measures that are relevant to the organization vs. measures that are relevant to users and the community. |
|
Approval |
In a traditional setting, we need to gain approval for minor decisions. HCD empowers employees to learn through action. |
|
Teams |
Homogeneous teams are most common in a traditional setting, whereas HCD focuses on diversity and inclusion. |
|
Projects |
Traditionally, teams work with a waterfall approach. HCD is iteratively developing ideas, making decisions, and delivering outcomes. |
Design Thinking and HCD are often used interchangeably, but there are differences between the two. IDEO identifies three HCD phases:
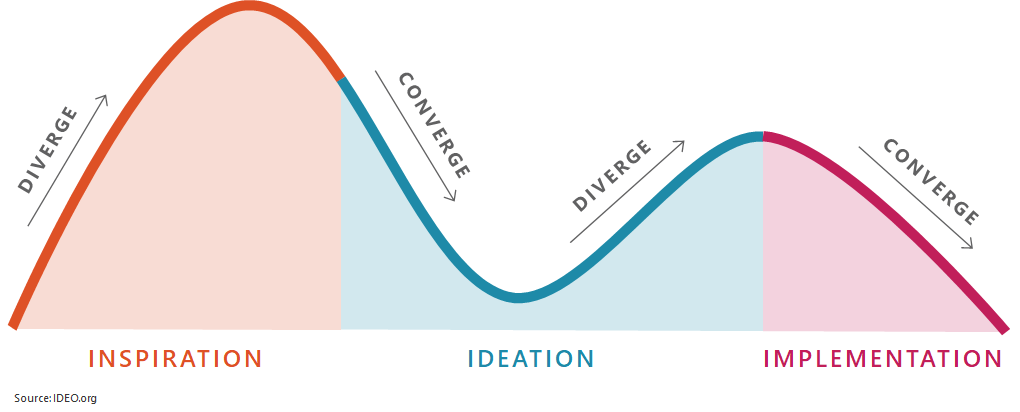
Design Thinking
If you overlay HCD with Design Thinking, you can see how the two approaches work with one another:
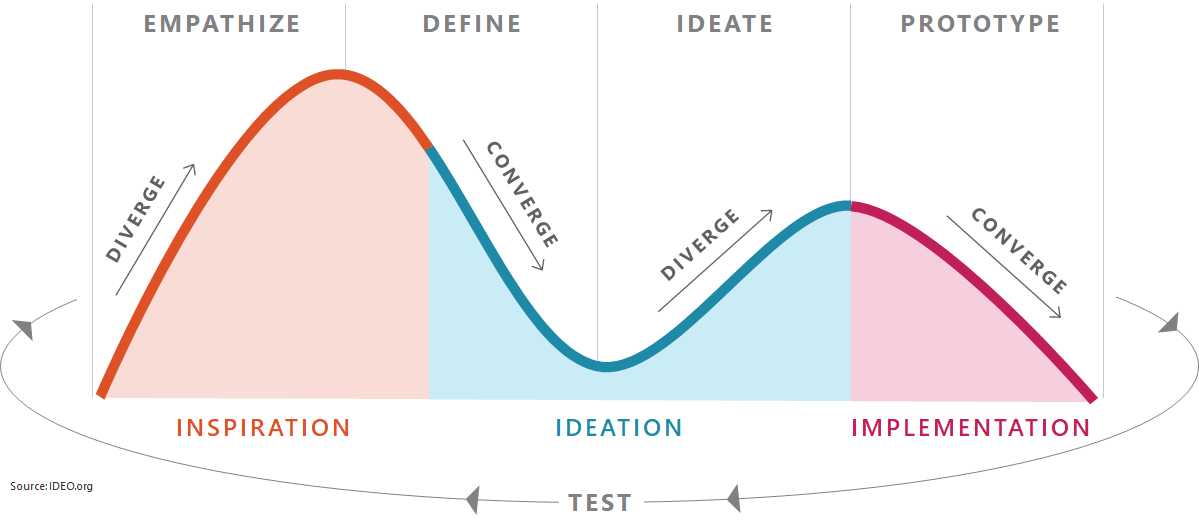
Human-Centered Design (HCD)
So how can we leverage this knowledge and reinvent our learning to be more intentional? Here are some ideas to get you started.
HCD doesn’t have to be time-consuming or difficult. Reinvent your learning experiences by working first with your learners and identifying their needs. Unsure of where or how to start your HCD session? Reach out to an Ardent expert to get your HCD sessions started off in the right direction.
These Stories on Design Thinking